Pneumatic conveyors use compressed air to move granular and powdered products with minimal damage, adjustable speed, and lower costs compared to other systems. They automate material handling processes. There are several types of pneumatic conveyors, including dilute phase, dense phase, vacuum, and pressure conveyors. In this pressure vs vacuum conveyor guide, we are focusing on dense phase conveyors, specifically on the difference between pressure and vacuum dense phase conveyors.
To begin with, dense phase conveying is a material handling process that moves bulk solids through a closed pipeline using high-pressure gas or air.
Selecting the right conveying system is critical for efficient material handling. Two popular methods are dense phase pressure and vacuum conveying. Choosing the best option depends on factors like material properties and distance. Before you get into the difference between the two, let’s take a look at the benefits dense phase pneumatic conveyors have to offer:
A] Benefits Of Dense Phase
Dense phase pneumatic conveying system is a material handling method that offers several advantages over other conveying methods. Some of these benefits include:- Reduced material degradation: They can help reduce degradation of material that occurs during transport, which is particularly important for delicate or fragile materials.
- Lower energy consumption: Since these conveying systems use less energy compared to other conveying methods, it is a more cost-effective option.
- Increased efficiency: These conveyors are used to move larger quantities of material over longer distances with fewer transfers. This can increase overall efficiency and productivity.
- Minimal dust emission: These systems can reduce the dust emission occurring during material transport, improving worker safety and reducing the need for cleanup.
- Greater control over material flow: They offer a greater control over material flow and speed, allowing for more precise process control and improved product quality.
Make the Right Choice: Pressure or Vacuum Conveying
B] What Is Pressure Dense Phase
In pressure conveying systems, the materials are transferred pneumatically through a closed pipeline using high-pressure gas or air. The system uses a rotary airlock feeder valve to ensure a continuous and controlled flow of materials into the pipeline. The system’s power is typically generated from the positive or negative pressure of the airflow, which allows for a smooth transfer of materials with minimal wastage and loss. This makes pressure conveying an efficient and cost-effective method for transporting bulk solids over long distances.
1. How Does Pressure Dense Phase Work?
The components are first pumped into the pressure vessel through the rotary airlock. Once the pressure tank has reached its capacity, the inlet and vent valves are sealed, and high-pressure air is gradually released. The material is conveyed to the receiver by high-pressure air, where the material is separated from the air by a filter or other device. Air volumes and speeds are controlled by valves and sensors. At the end of the conveying cycle, when the specified low-pressure setting is achieved, the air supply is shut off, and the extra air volume purges the pressure tank and the conveying line.
When transporting bulky materials over longer distances, pressure-conveying machines are usually preferred. However, it is important to note that pressure conveying systems may require specialised equipment, such as a rotary valve and vent system, which can add to the initial cost. Despite this, the long-term benefits of using a pressure conveying system for transporting bulky materials over longer distances often outweigh the initial investment.
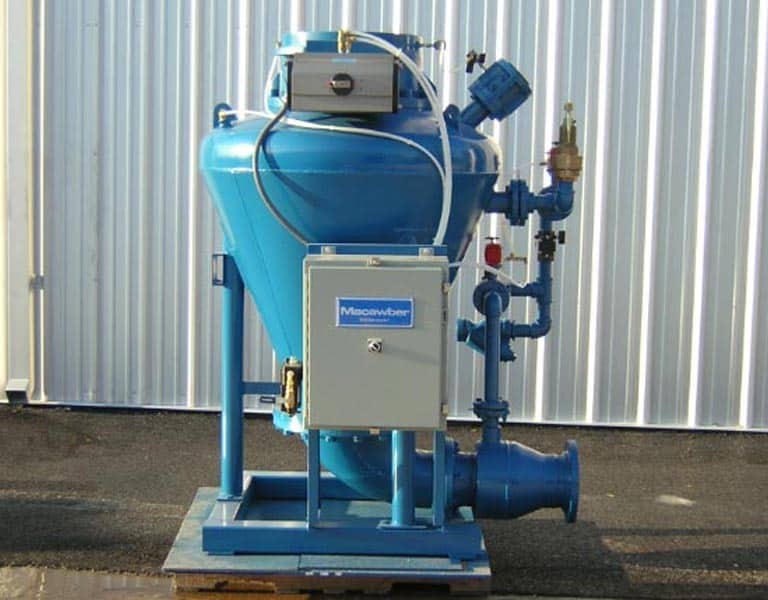

2. Reasons To Choose Pressure Conveying
- Pressure conveying is better suited for long-distance transportation of materials compared to vacuum conveying.
- Pressure conveying systems can handle materials with higher bulk densities and larger particle sizes compared to vacuum conveying.
- Pressure conveying is more energy-efficient than vacuum conveying, as it requires less power to move materials.
- Pressure conveying is better suited for materials that are cohesive or prone to bridging.
- Pressure conveying systems can operate at higher pressures, allowing for greater flexibility in system design.
- Pressure conveying systems can handle abrasive materials better than vacuum conveying systems.
- Pressure conveying is better suited for materials that require high flow rates.
Make the Right Choice: Pressure or Vacuum Conveying
C] What Is Vacuum Dense Phase
Dense phase vacuum conveying systems are pneumatic conveying systems that are specifically built for the pneumatic conveying of powders and bulk materials through pipelines or ducts known as transportation lines. A vacuum system’s essential features are the pick-up nozzle, the moving line, the receiver, and the vacuum generator, which serves as the power source. The negative pressure required for drawing the substance through the conveying line and into the receiver is generated by the vacuum generator. The vacuum generator used determines the highest negative pressure produced and the total capability of the system, as well as its efficiency and general working characteristics. The vacuum generator’s air movement transports the substance through the conveying tubes and into the receiver.
1. How Does Vacuum Dense Phase Work?
For moving materials that tend to pack or plug into a pressure system, vacuum methods are typically chosen. They are also the most popular option. However, vacuum conveyors are not a preferred choice for transporting materials over long distances. Vacuum conveyors have a maximum horizontal distance of 50 feet and a maximum horizontal distance of 200 feet because they work at or below air pressure. Vertical distances and piping curves also decrease the actual horizontal distance. The vacuum generator’s air movement transports the component through the conveying lines and into the receiver. The material descends into the recipient hopper due to gravity there. To clear dust and safeguard the vacuum generator, internal filters isolate the substance from the air. The material can be delivered from the recipient to its ultimate location using a variety of techniques depending on the application, such as dump gate basic slide valves, pneumatically controlled dump gates, or air lock rotary valves.
2. Reasons To Choose Vacuum Conveying
- Vacuum conveying is better suited for handling fragile materials and those prone to degradation, as it uses low pressure to move materials.
- Vacuum conveying can operate at higher vacuum levels, making it better suited for applications where a low oxygen environment is required, such as food processing or pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Vacuum conveying systems require less maintenance compared to pressure conveying systems, as there are fewer moving parts.
- Vacuum conveying is generally less expensive to install and operate compared to pressure conveying, as it requires less specialised equipment.
- Vacuum conveying can be used for both short and long-distance transportation of materials, making it a more versatile option.
- Vacuum conveying systems are better suited for materials that are fine, dusty, or have a tendency to create airborne dust, as they can be contained and controlled more easily.
- Vacuum conveying can be used for both batch and continuous conveying operations, making it a more flexible option for material handling.
D] Factors To Consider While Choosing Between Pressure Dense Phase Conveyors & Vacuum Dense Phase Conveyors:
Listed below are some factors to consider while choosing between pressure dense phase pneumatic conveying and vacuum dense phase pneumatic conveying systems:- Material properties: Material properties like particle size, shape, and density influence the flow characteristics of materials and the suitable conveying method. Pressure conveying is ideal for dense and heavy materials, while vacuum conveying is better for lighter and friable materials.
- Distance and height of transport: Distance and height of transport affect energy consumption, with pressure conveying being suitable for longer distances and higher elevations, and vacuum conveying being more appropriate for shorter distances and lower elevations.
- Required throughput and capacity: The required throughput and capacity play a crucial role in determining the appropriate conveying method. Pressure conveying is ideal for high-capacity systems, while vacuum conveying is more suitable for low to medium capacity systems.
- Operating cost: Operating costs, including energy consumption and maintenance, can vary between pressure dense phase and vacuum dense phase pneumatic conveying systems, and considering these costs is important in choosing the most efficient and cost-effective option for a particular application.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Environmental and safety considerations are important factors to consider because the conveying process may generate dust, noise, or other hazards that need to be addressed. The choice of conveying method can impact these factors, and it is important to select a method that meets environmental and safety requirements. For example, vacuum conveying may be preferable in situations where dust containment is critical, while pressure conveying may be better suited to handle hazardous materials.
Make the Right Choice: Pressure or Vacuum Conveying
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of pneumatic conveying equipment can assist your business in meeting potential development goals by enabling you to work more effectively as you convey materials in and out of distribution and storage areas. Pneumatic Conveying system, be it pressure or vacuum, provides efficient and dust-free conveying and is an excellent choice for your business. Where pressure is preferred for bulky materials and longer distances, vacuum has the tendency to move materials in an enclosed tube. In contrast with other techniques, pneumatic conveying is an efficient way to manage and transport various types of high-volume granulated and powdered goods with minimum loss and at a lower cost.
Kedar Kamath
Kedar Kamath is a highly accomplished bulk material handling professional with 14+ years of experience at Macawber Engineering Systems India Pvt Ltd. Starting as a junior sales engineer, he progressed to his current role heading Business Development and Sales. His expertise encompasses proposals, estimations, sales, marketing, design engineering, project execution, and factory operations. Mentored by industry leaders, Kedar's technical acumen (B.Tech in Electrical Engineering, VJTI, Mumbai) and innovative approach deliver tailored solutions. He's passionate about sustainable practices and driving excellence within the industry.